
Measurement is a systematic process of determining the attributes of an object. It ascertains how fast, tall, dense, heavy, broad, something is. However, one can make measurements of physical attributes only and if one has to measure those attributes which cannot be measured with the help of tools. That is where the need for evaluation arises. It helps in passing value judgement about the policies, performances, method, techniques, strategies, effectiveness, etc. of teaching.
Measurement provides a solid base to make an evaluation, as you have something concrete to make a comparison between the objects. Further, Evaluation has a crucial role to play in reforming the learning and teaching process and suggesting changes in the curriculum.
In this post, we will talk about the differences between measurement and evaluation.
| Basis for Comparison | Measurement | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Measurement refers to the process of delegating a numerical index, to the object in a meaningful and consistent manner. | Evaluation is when the comparison is being made between the score of a learner with the score of other learners and judge the results. |
| Observations | Comprises the observations which can be expressed numerically. | Comprises of both quantitative and qualitative observations. |
| Involves | Assignment of numerals according to certain rules. | Assignment of grades, level or symbols according to established standards. |
| Concerned with | One or more attributes or features of a person or object. | Physical, psychological and behavioral aspects of a person. |
| Answers | How much | How good or how well |
| Logical assumption | It does not convey any logical assumption about the student. | Logical assumption can be made, about the student. |
| Time and Energy | Requires less time and energy | Requires more time and energy |
| Scope | Limited | Wide |
| Orientation | Content oriented | Objective oriented |
When one of the sets of numerals is assigned to each set of objects, be it person or commodity, as per the accepted rules or standards and described in standard words, units and symbols, so as to characterize the status of that object it is called as measurement. In education, measurement implies the quantitative assessment of the student’s performance in an exam.
It is a mechanical process, which involves the systematic study of the attributes with the help of appropriate assessment tools. It transforms the variable into variate, which is effective in making deductions. For instance, Intelligence is measured in terms of IQ, and the result variable is measured as scores.
Further, it is helpful in comparing the performance of various students as well as in highlighting their positive and negative points.
Evaluation can be defined as the act of assigning value to the measure. It is a systematic and continuous process wherein the analysis of the outcome derived from the measurement of the characteristic of the object, person or activity is performed as per the defined standards. Further, the relative position of the person, object or activity is ascertained, on the basis of the characteristic.
In evaluation. what we do is, we pass judgement regarding how suitable, desirable or valuable something is. In education, evaluation alludes to the overall assessment of the progress of the student, with respect to:
It acts like an ‘inbuilt monitor’, within the system, that tends to review the learning progress, at various points in time. It also provides feedback on various aspects of the educational systems, such as on teaching to the teachers and on learning to the learners.
So we can conclude that:
Evaluation = Quantitative description + Qualitative Description + Value Judgement
where, the quantitative description includes facts and figures and the qualitative description includes ranking, weightage and value.
Hence, in evaluation, the knowledge of the student/learner is not the only aspect which is considered, rather all the aspects which are important for his/her development are taken into consideration.
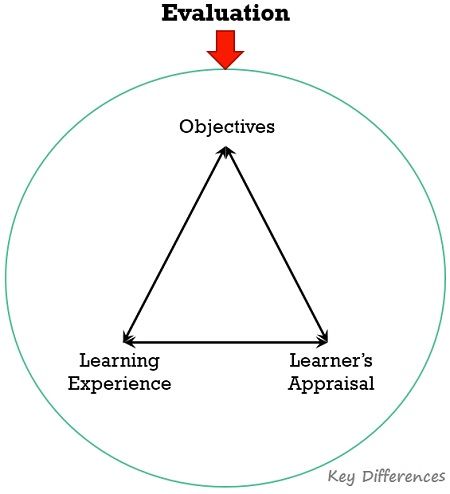
So, evaluation covers four different aspects, namely:
It aims at ascertaining the progress of the student, reforming the system of education and increasing the answerability for outcomes.
Check out the point stated below, to understand the differences between measurement and evaluation:
Let us take an example, in which we will take some attributes of a student of 5th standard, to measure and evaluate
| Attribute | Measurement | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | 42 kg | Fat |
| Running speed (100 meter) | 40 seconds | Fast |
| Marks Obtained (out of 500) | 350 marks | Grade B |
Explanation
In the first case, the measurement of weight of the student is 42 kg, wherein kg denotes the rule according to which weight is to be measured. On the other hand, in case of evaluation, the weight is categorized into three groups, i.e. 18 kg to 28 kg is considered as thin, 28 kg to 38 kg is considered as average, while 38 kg to 48 kg is considered as Fat.
Similarly, in the second case, we measured that the student covered the 100-meter distance in just 40 seconds, wherein m/s is the unit of measurement. Now when we evaluate, the running speed is categorized into three parts, i.e. up to 50 seconds fast, 50 to 75 seconds average and more than 75 seconds is slow.
In the last case, the student scored 350 marks in the test out of total 500 marks, wherein marks are the unit of measurement. Now when we evaluate, the mental ability is divided into three parts, in which the students scoring 400 to 500 marks will be allotted Grade A, 300 to 400 marks will be allotted Grade B and students scoring less than 300 marks will be allotted Grade C.
So, what we have done here is, we divided the weight, running speed, marks into different grades and then made a comparison of the actual achievement of the student with the predetermined standards for the purpose of evaluation.
So, with the above discussion, you might have understood that evaluation is an indispensable part of the educational system which includes measurement. It helps in making improvement in teaching and learning, establishing objectives, determining learning experiences and assessing the performance of the learner.